The Office of Information Security observes a trend in which criminals use a compromised email account to trick victims into divulging their WUSTL Key password. In this scam, criminals took over a legitimate email address from UT Health San Antonio and used it to send phishing emails. Victims who click on the phishing link are taken to a fake WUSTL Key login.
To show you how convincing the fake login screen is, compare it with the legitimate WUSTL Key login screen below:
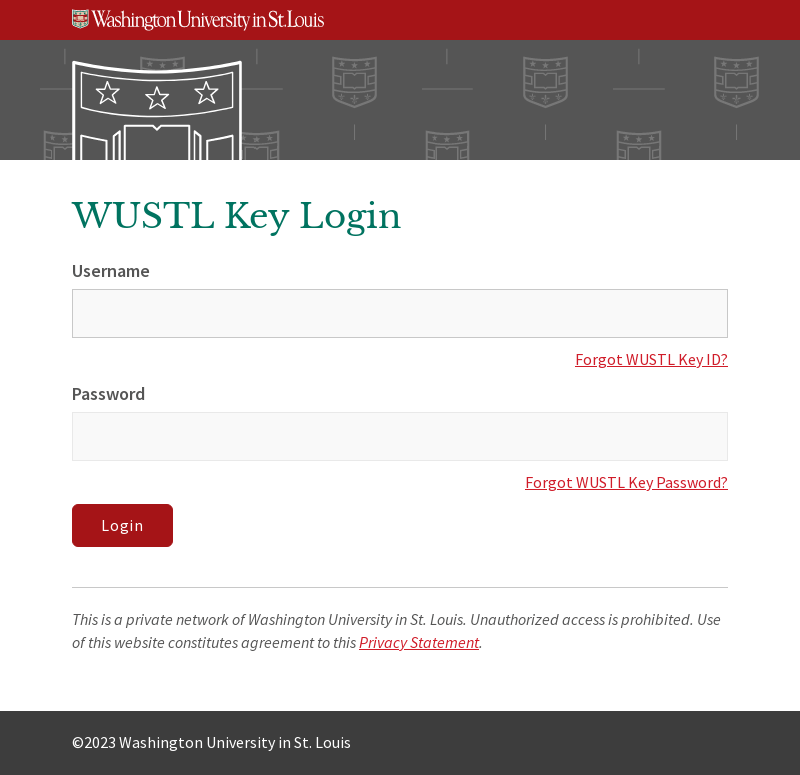

Pretty believable, right? There is a dead giveaway, though. A legitimate WUSTL Key login screen always has “connect.wustl.edu” at the beginning of its URL. The fake login URL (not pictured) in our example is not even close to what it should be. If you see a message like the one below, please do not interact with any links or enter your WUSTL Key. Simply report it using the Phish Alert Button (PAB) in your Outlook interface. It is always best to exercise caution and report anything remotely suspicious. Our team will analyze all submissions and return them to you if they are determined to be safe. Below, we dissect the phishing email to reveal its red flags.

- The email address is outside of WashU.
- The subject line is vague. Many scammers try to make phishing content as generic as possible so that it might apply to a lot of people.
- Urgency. Scammers often make urgent requests to make victims rush into their trap.
- The signature is suspicious. Why would an outside email address sign with “Washington University”?
Avoid this and other scams by following our ten phishing safety tips and related guidance below.
10 Phishing Safety Tips
- Don’t click. Instead of clicking on any link in a suspicious email, type in the URL or search wustl.edu for the relevant department or page. Even if a website and/or URL in an email looks real, criminals can mask its true destination.
- Be skeptical of urgent requests. Phishing messages often make urgent requests or demands. When you detect a tone of urgency, slow down and verify the authenticity of the sender and the request by using official channels rather than the information provided by the sender.
- Watch out for grammar, punctuation, and spelling mistakes. Phishing messages are often poorly written. Common hallmarks of phishing are incorrect spelling, improper punctuation, and poor grammar. If you receive an email with these problems, it may be a phishing attempt. Double-check the email address of the sender, don’t follow any links, and verify the authenticity of the request using official channels.
- Keep your information private. Never give out your passwords, credit card information, Social Security number, or other private information through email.
- Pick up the phone. If you have any reason to think that a department or organization really needs to hear from you, call them to verify any request for personal or sensitive information. Emails that say “urgent!”, use pressure tactics, or prey on fear are especially suspect. Do an online search for a contact phone number or use the contact number published in the WUSTL directory.
- Use secure websites and pay attention to security prompts. Always check if you are on a secure website before giving out private information. You can determine whether a website is secure by looking for the “https:” rather than just “http:” in the Web address bar or for the small lock icon in the Internet browser. If your browser cannot validate the authenticity of the website’s security certificate, you will be prompted. This is frequently a telltale sign of fraud, and it would be a good time to pick up the phone or report a suspicious message.
- Keep track of your data. Regularly log onto your online accounts and make sure that all your transactions are legitimate.
- Reset any account passwords that may have been compromised.
- Know what’s happening. Visit the Office of Information Security Alerts page often.
- Report it. If you are a victim of an email scam, report it to our office by using the Phish Alert Button (PAB). When you report a phishing attack, we will investigate it and, if necessary, remove other instances of the attack from our systems. Reporting the attack will help protect others and our institution.
Additional Resources
Phishing | Office of Information Security | Washington University in St. Louis
Phishing 101 | Office of Information Security | Washington University in St. Louis