In each issue of the newsletter, we will feature, discuss, and dissect a scam that has appeared on our campus. These scams are “real” attempts to infiltrate our systems and/or gain access to sensitive and personal information of individuals in our community. By sharing these examples with our readers, we hope to enhance your awareness of existing threats and prepare you to detect novel threats as they arise.
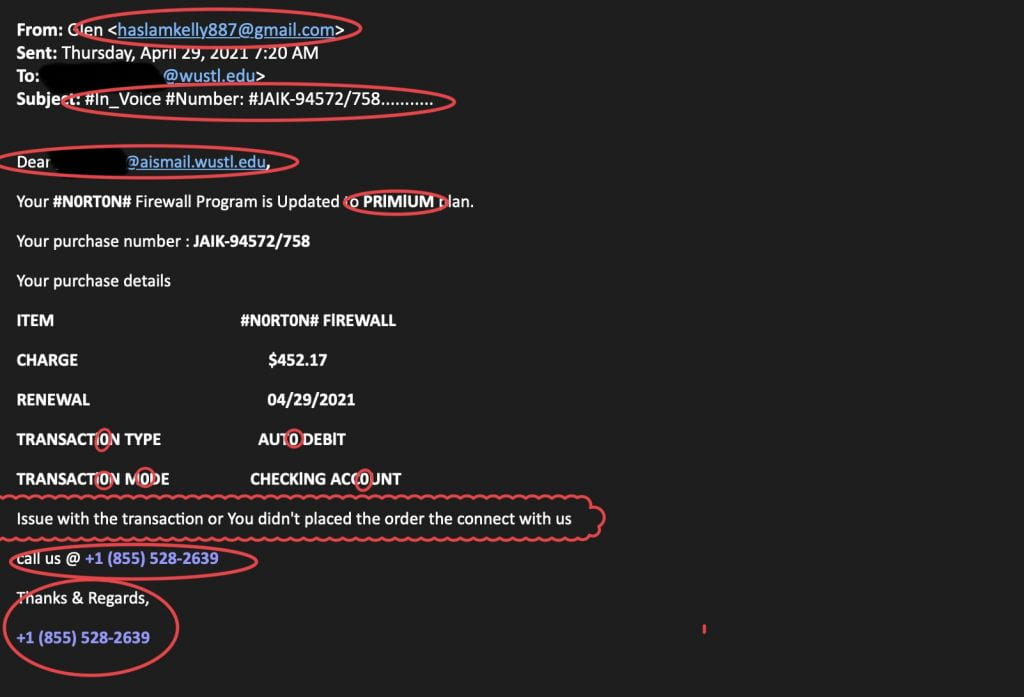
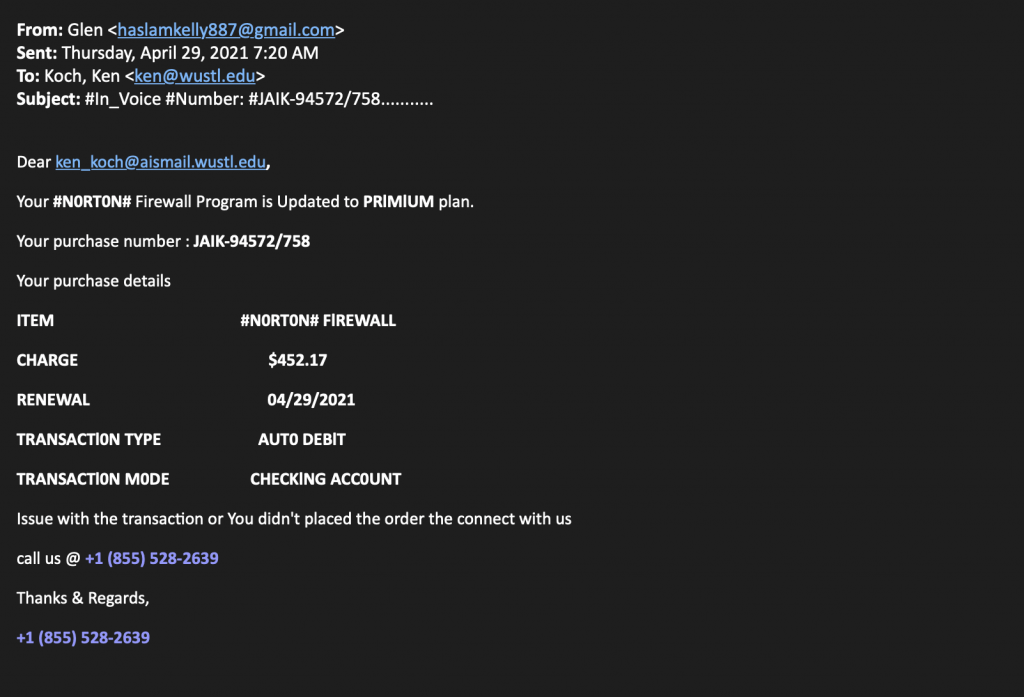
Take a look at the message below and try to identify all of the security “red flags” that you can. We’ve identified at least eight red flags in this email. How many can you spot?
- Sender: Glen, haslamkelly887@gmail.com
“Glen” purports to be affiliated with Norton’s Firewall Program but is sending a fake invoice from a personal e-mail address. If this was a legitimate invoice, it would have originated from the company.
- Subject: #ln_Voice #Number: #JAIK-94572/758……..
This subject line is basically unintelligible to the customer. A legitimate invoice from a real company would likely be clear and informative. The “number” may make it seem formal or official, but the recipient should remain skeptical of this poorly communicated subject.
- The salutation does not include the recipient’s name, and instead includes an e-mail address.
- Grammar and spelling errors
Poor grammar and spelling are common red flags in phishing messages. Here, “Premium” is misspelled as “PRIMIUM”, the sentence, “Issue with the transaction or You didn’t placed the order the connect with us,” is fraught with grammatical errors, and the letter ‘O’ appears to be typed with a zero in several places.
- Improper capitalization and punctuation
The request to “call us @ +1 (855) 528-2639” is incorrectly punctuated and capitalized.
- No-name closing
“Glen” didn’t sign off in the closing. There is no information about the sender or their position with Norton. Instead, the closing only reiterates the contact number posted just above it.
- Sense of urgency surrounding a failed transaction.
This email claims to have attempted and failed to complete an auto debit from a checking account in the amount of $452.17. The recipient may be alarmed by an unknown bill amounting to hundreds of dollars and try to reach out to the sender. Rather than engage with this malicious sender about a fake charge, simply report the message to our office, and we will investigate the issue.
- Lack of Norton branding and contact information
This message did not even attempt to mimic a legitimate Norton message using brand imagery or contact information. Norton is a large company, and their messaging is branded. Branding alone is not enough to establish credibility, however. Cybercriminals can easily fake branding elements to trick recipients into believing the message is real. In this case, the lack of branding paired with other red flags reveals that this is a phishing attempt and not a legitimate email.